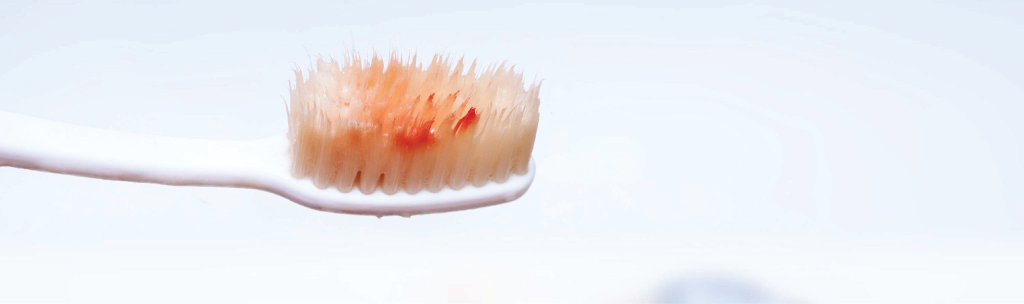
Gums are one of the areas most examined by dentists. Some patients visit without reason complaining of gum bleeding, while others mention encountering bleeding when brushing their teeth. Bleeding may signal a disease in your gums or bones, but various other factors can also cause the same bleeding. Understanding the source of your gum problems is the first step to alleviating your discomfort. In this guide, we will first address the main causes and symptoms of gum bleeding. In later sections, we will discuss treatment options and what you can do at home.
What Is Gum Bleeding?
Gum bleeding is not a standalone problem. It usually appears as a sign of gingival inflammation or a more serious gum issue. Everyone may experience occasional gum bleeding. Small amounts of bleeding often occur after brushing too hard and are not dangerous. However, recurring gum bleeding is often a warning sign of something serious and should always be checked.
What Are the Symptoms of Gum Bleeding?
Gum bleeding is among the easiest problems for dentists to identify. Usually noticed by gums turning red, bleeding may also manifest through various symptoms:
- Red, sensitive gums
- A bloody taste in the mouth
- Occasional pus discharge
- Bad breath
- Gum recession
- Increased tooth sensitivity
- Pain and tenderness
- Discomfort when eating
What Causes Gum Bleeding?
Bacterial infections in the gums produce toxins that inflame the gum tissue. These toxins gradually swell the gums and turn them more red than normal. This leads to weakening and recession of the gums. Gum bleeding in children is less common than in adults; in children, the main cause is usually injury from incorrect brushing. In adults or the elderly, bleeding is more often linked to other conditions. Common causes of gum bleeding in adults and older people include:
Trauma: Inserting hard foreign objects into the mouth can injure the gums and cause bleeding.Irritation: Acids or chemicals in products like chewing gum or mouth sprays can irritate the gums, leading to bleeding.Oral wounds: Infections of mouth sores can spread to the gums and cause them to bleed.Dental diseases: Problems in teeth or gums increase the risk of bleeding.Blood disorders: Diseases such as leukemia or clotting disorders are known to cause gum bleeding.Systemic illnesses: Conditions like liver or kidney disorders, and diabetes, can manifest as gum bleeding.Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can lead to gum bleeding.Cancer: Bleeding in the gums may be directly related to cancer, especially cancers affecting blood values.Vitamin deficiency: Vitamins C and K are key for gum health; their deficiency can lead to bleeding disorders.Medications: Some medications cause gum bleeding as a side effect. For example, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or prolonged use of blood-thinners can induce gum bleeding.Teething: Teething is a main cause of gum bleeding in infants. Adults may also experience gum bleeding when wisdom teeth erupt.
How Is Gum Bleeding Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of gum bleeding is made by a dental specialist. Usually after a comprehensive oral examination, the problem is identified. In some cases, your dentist may request further tests:
Possible tests your dentist may order to clarify the cause of gum bleeding:
- Dental X-ray
- Jaw X-ray
- Blood analysis
- Blood sugar test
- Bleeding and clotting time tests
If your dentist suspects an underlying condition, these tests help bring clarity.
How Is Gum Bleeding Treated?
 Gum bleeding is a common problem in the community. Since many different diseases can cause gum bleeding, there is no single treatment for everyone. Treatment varies depending on the cause of bleeding and the patient’s symptoms. Possible treatments include:
Gum bleeding is a common problem in the community. Since many different diseases can cause gum bleeding, there is no single treatment for everyone. Treatment varies depending on the cause of bleeding and the patient’s symptoms. Possible treatments include:
- Mouthwash: If no other disease underlies the problem, using a suitable mouthwash can be an effective solution for gum bleeding.
- Medication: Dentists often prescribe medications—typically pain relievers—to reduce the painful, distressing symptoms of gum bleeding.
- Gum surgery: If recession or persistent inflammation has occurred in your gums, your dentist may recommend gum surgery. Thus, surgery can be one of the treatment methods.
- Gum aesthetics: Worn or irritated gums may develop an unattractive appearance over time. After gum recession, aesthetic gum procedures can both improve appearance and help prevent further bleeding.
How Can Gum Bleeding Be Stopped?
Preventing gum bleeding is not as difficult as it may seem. By cleaning your teeth properly, you can help keep your gums healthy. Beyond basic care, pay attention to the following to stop bleeding:
- Reduce tea and coffee consumption.
- Consume calcium-rich foods.
- Perform daily gum massage with clove oil.
- Brush your teeth regularly.
- Visit your dentist routinely.
Frequently Asked Questions About Gum Bleeding
Below are answers to common questions about gum bleeding.
What Does Gum Bleeding Signal?
For specialists, bleeding gums often signal another underlying disease. If you experience gum bleeding, likely causes include:
- Diabetes
- Gum disease
- Tooth decay
- Leukemia
- Systemic illnesses
My Gums Are Bleeding—What Should I Do?
People may occasionally experience gum bleeding. What matters is how much bleeding and how long it lasts. If you have prolonged gum bleeding, we recommend making an appointment with your dentist as soon as possible.
What Do Healthy Gums Look Like?
Healthy gums are firmly attached around the teeth and have a light pink color. Other features of healthy gums include:
- A “orange peel” texture on the gum surface.
- No bleeding when brushing.
- No pain or swelling.
How Can You Tell Unhealthy Gums?
Unhealthy gums have turned from pink to red and are swollen. Additional features include:
- Dark red color.
- Bleeding gums in the morning.
- Heavy gum bleeding at night.
- Gum recession.
- In advanced gum problems, bad breath may also occur.
- Swelling in the gums.
Which Vitamin Deficiency Causes Gum Bleeding?
Vitamins C and K are key for nourishing our gums. Deficiency in either of these vitamins can lead to gum bleeding.
Why Do Gums Bleed When Brushing?
- There are many reasons for gum bleeding while brushing. Determining the underlying cause requires a full oral examination.
- What helps gum bleeding? Effective measures include: avoiding sugary foods and drinks, drinking plenty of water, avoiding tobacco products, and treating the underlying cause.
How to Stop Gum Bleeding Naturally?
You can stop gum bleeding using natural methods. Some of these methods are:
- Clove: Massaging your gums with clove can help soothe and relax the gum tissue.
- Garlic: Garlic has antibacterial properties. You can massage your gums with two cloves of garlic or chew garlic directly.
- Saltwater: Gargling with salt water is highly effective in stopping gum bleeding.