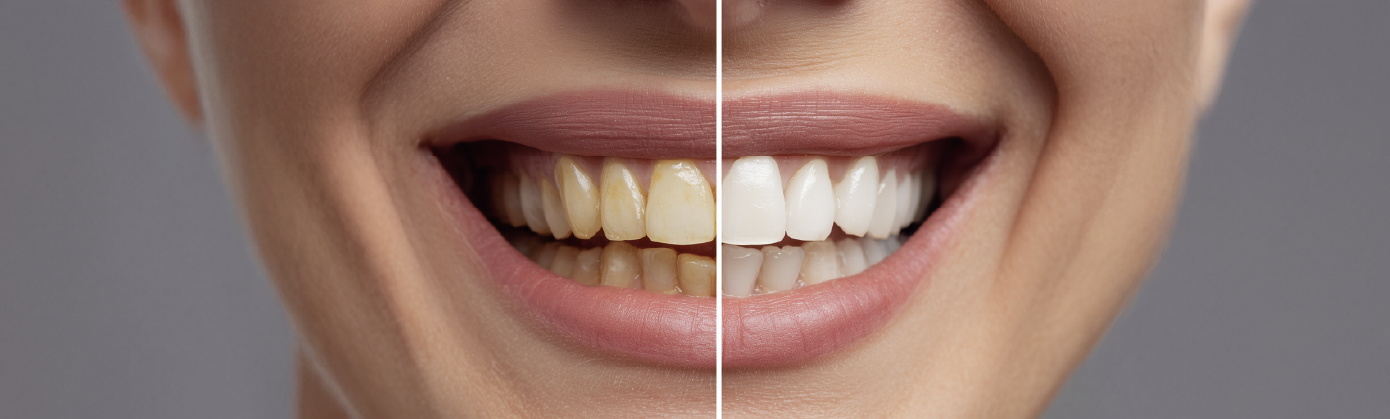
Dental erosion is defined as the loss of hard tissue from the teeth. Also known as dental acid erosion, this condition arises when the enamel is worn away and damaged by acids. It presents with symptoms such as tooth sensitivity and discoloration. If this condition progresses, you may require fillings or veneers. Thanks to early diagnosis and preventive measures, it is possible to halt the progression of erosion. Therefore, to avoid encountering this problem, it is important to attend regular dental check-ups.
What are the symptoms of dental erosion?
Symptoms of dental erosion generally include:Sensitivity: As enamel wears away, dentin becomes exposed, causing sensitivity to cold, heat, or sweet foods and drinks.Shiny/Smooth Appearance: With the enamel layer eroded, teeth acquire a shiny and smooth surface.Tissue Loss: As wear progresses, noticeable loss of tooth structure occurs. Teeth appear smaller and take on a pointed or irregular shape.Discoloration: The exposed dentin layer can turn yellowish or brownish, leading to tooth discoloration.Cavity Formation: Eroded teeth are more prone to decay.Pain: In advanced stages, severe enamel loss can lead to pain. If you observe any of these signs of dental erosion, it’s important to see your dentist as soon as possible. Early intervention can prevent serious deterioration of your dental health.
What causes dental erosion?
Numerous factors can contribute to the development of dental erosion, including:
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): In reflux patients, stomach acid can flow back into the mouth and damage teeth.
- Bulimia Nervosa: In bulimia, vomiting brings stomach acid into the mouth, harming the teeth.
- Medication Use: Certain medications (e.g., vitamin C, aspirin) can impair salivary gland function, leading to dry mouth and an acidic environment.
- Dry Mouth Insufficient saliva flow deprives teeth of protective effects.
- Overbrushing: Excessive pressure when brushing and the use of abrasive toothpastes can contribute to erosion.
- Genetic Factors: Some people are born with thinner or weaker enamel.
- Pregnancy: Frequent nausea and vomiting during pregnancy can expose teeth to stomach acid.
- Acidic Foods and Drinks: Consuming acidic beverages (cola, fruit juices, wine, lemon-flavored drinks) or foods leads to enamel erosion and is a common cause of dental erosion.
How can acid erosion be prevented?
Limiting the consumption of acidic foods and drinks is the most important step in preventing erosion. Reduce or eliminate acidic beverages such as soft drinks, fruit juices, and sports drinks. If you do consume them, use a straw and swallow quickly to minimize contact with your teeth. After consuming acidic items, rinse your mouth with water. However, avoid brushing your teeth immediately afterward, as acid temporarily softens enamel, and brushing right away can accelerate wear. Increasing saliva flow also helps prevent erosion. Saliva neutralizes mouth acids, so chewing sugar-free gum, drinking water, or eating salty snacks can stimulate saliva production and protect your teeth. Use fluoride toothpastes and mouthwashes recommended by your dentist to strengthen enamel and guard against dental erosion.
Nutritional recommendations for preventing dental erosion
Diet plays a crucial role in protecting against erosion. Consider the following tips:
- Avoid Acidic Beverages: Limit consumption of sodas, fruit juices, and sports drinks.
- Reduce Sugar Intake: Sugary foods and drinks create an acidic environment in the mouth. Lowering sugar helps prevent erosion.
- Consume Dairy Products: Milk, yogurt, and cheese have a neutralizing effect on mouth acids. Regular intake is beneficial.
- Drink Green Tea: Green tea can boost saliva production and help maintain oral pH balance.
- Eat Firm Fruits in Slices: Slicing apples or pears releases less acid than biting them whole.
- Choose Salty Snacks: Salty foods stimulate saliva flow, helping to neutralize acids.
- Chew Gum Instead of Hard Candies: Hard candies can abrade enamel, whereas chewing gum increases saliva production.
- Drink Plenty of Water: Staying well-hydrated supports saliva production and enamel protection.
- Rinse with Water After Acidic Intake: Rinsing removes acid residues from the mouth.
How is dental erosion treated?
Treatment for enamel erosion varies by severity. If diagnosed early, further tissue loss can be prevented. In advanced cases, lost tooth structure can be restored through various methods. First, identify and eliminate the factors causing erosion—for example, adopting a healthier diet, treating dry mouth, or managing reflux. If sensitivity is present in worn areas, special liners or varnishes can be applied. Fluoride gels and varnishes strengthen enamel and help reduce erosion. In more advanced cases, lost dental tissue may be restored with fillings, crowns, or veneers. Tooth-colored composite fillings are often used to rebuild eroded areas and improve appearance. For severe tissue loss, full crowns may be recommended. In extreme cases where tooth shape and bite are compromised, comprehensive dental treatment may be necessary. If you want to overcome this problem, visit our clinics. Prevent dental erosion with regular dental check-ups!